This document is a constituent part of the Cloud Data Management Capabilities (CDMC™) model (“the Model”) and is provided as a free license to any organization registered with EDM Council Inc. (“EDM Council”) as a recipient (“Recipient”) of the document. While this is a Free License available to both members and non-members of the EDM Council, acceptance of the CDMC Terms of Use is required to protect the Recipient’s use of proprietary EDMC property and to notify the Recipient of future updates to the Model.
CDMC™ and all related materials are the sole property of EDM Council Inc. All rights, titles and interests therein are vested in the EDM Council. The Model and related material may be used freely by the Recipient for their own internal purposes. It may only be distributed beyond the Recipient’s organization with prior written authorization of EDM Council. The Model may only be used by the Recipient for commercial purposes or external assessments if the Recipient’s organization has entered into a separate licensing and Authorized Partner Agreement with EDM Council governing the terms for such use.
Please accept these CDMC™ Terms of Use by registering at:
https://app.smartsheet.com/b/form/6e2b0bf4a3024affb98daad174b08483
Introduction
Purpose
Digital transformation is fundamentally changing how we do business – personally and professionally. Much of this transformation is taking place in the cloud environment across the globe. Cloud implementations are occurring in all sectors across all industries. There are many benefits of managing and storing data in a cloud environment, including cost savings, flexibility, mobility, improved information security, increased collaboration, and realizing new insights within an organization’s data assets.
As with any new technology, cloud computing entails many challenges. New cloud implementations face a variety of data, technology and planning difficulties. There remains a lack of consistent industry best practices for applying data management capabilities during migrations to and operations in single, multiple and hybrid cloud environments.
Consequently, an organization will likely face cost and complexity risks when adopting cloud computing technologies. Adoption can be especially difficult for regulated entities that must demonstrate precise, consistent data control in both on-premises and cloud environments. Cloud service providers (CSPs) and technology providers also face complexity as they seek to understand the data management priorities of organizations, resulting in challenges to improving their cloud implementations.
The Cloud Data Management Capabilities (CDMC™) Framework defines the best practice capabilities necessary to manage and control data in cloud environments. The creation of this framework represents an important milestone in the global adoption of industry best practices for data management. The overall objective is to build trust, confidence and dependability for the adoption of cloud technologies, offering benefits to each of the constituencies within the cloud ecosystem:
- Cloud Service and Technology Consumers – provides a structured framework of auditable processes and controls, especially for sensitive data.
- Cloud service providers – provides requirements and controls that can be automated within CSP platforms, accelerating adoption and increasing market confidence.
- Application, Technology and Data Providers – applies standard, certified CDMC capabilities and controls to services and solutions to ensure a high degree of reliability and operational effectiveness.
- Consultants and System Integrators – enables training and assessments, gap analysis, strategy development, and execution services for end clients adopting cloud technologies.
- Regulators – provides industry guidance for auditing and validating key cloud environment controls, especially for sensitive data.
CDMC is a best practice assessment and certification framework for managing and controlling data in single, multiple, and hybrid cloud environments. CDMC is used to assess the capabilities of an organization that are necessary to support controlled integration and migration to the cloud environments. The framework focuses and expands on capabilities critical to controlling important and sensitive data and highlights features of contemporary cloud platforms that present opportunities for standardization and automation of data management and control.
Though CDMC is a standalone framework, it assumes that an organization already has a strong foundation of data management capabilities. A broader set of capabilities is covered in other frameworks such as the Data Management Capability Assessment Model (DCAM®) of the EDM Council. Effective data management fundamentals, together with the features and capabilities defined in CDMC, will enable an organization to build trustworthy and secure cloud environments—both now and well into the future.
Approach
CDMC was produced by the EDM Council CDMC Work Group formed in May 2020 with over 300 individual business executives, engineers, technologists and data professionals. The group includes participants from over 100 organizations across the globe, including major CSPs, technology service organizations, privacy firms and major consultancy and advisory firms. The objectives of the initiative were to:
- Develop a framework that provides direction and guidance on core data management capabilities in cloud data management aligned with industry best practices.
- Develop a consistent CDMC scoring model for industry organizations to measure maturity and readiness against the cloud data management capabilities.
- Collaborate with cloud service and technology providers and industry organizations on a set of priorities for accelerating capabilities for cloud migration and implementations while allowing cloud service and technology providers the opportunity to apply their unique innovations and services to meet these industry requirements.
- Establish methods to continuously improve the CDMC Framework and facilitate training and education on these best practices.
The structure of CDMC and the approach to its creation leveraged the structure and approach of the DCAM® framework, which the EDM Council has maintained since 2014.
CDMC – A FRAMEWORK FOR CLOUD DATA MANAGEMENT
Many organizations must establish a broad set of controls to manage data responsibly and comply with applicable regulatory entities. Standards and best practices enable an organization to harness the enormous opportunity offered by cloud technologies while avoiding the challenges of developing and adapting home-grown controls and spending time on isolated feature requests between individual companies and CSPs.
Controlling data in cloud environments requires a complex set of data management capabilities:
- An organization must establish clear accountability, controls and governance for data migrated to or created in cloud environments.
- A critical requirement is always to know what data resides in cloud environments and the sensitivity of each of the data assets. Such tracking is essential to automating controls for data access and use. Tracking is also vital to enforcing the controls and maintaining evidence for required transparency, security, and protection levels.
- Data management controls must be established throughout the data lifecycle.
- Data assets must be fit-for-purpose and kept to required schedules for retention and archiving.
- As with on-premises data assets, the design of the data architecture and configuration of supporting technologies are important for ensuring that business objectives are met.
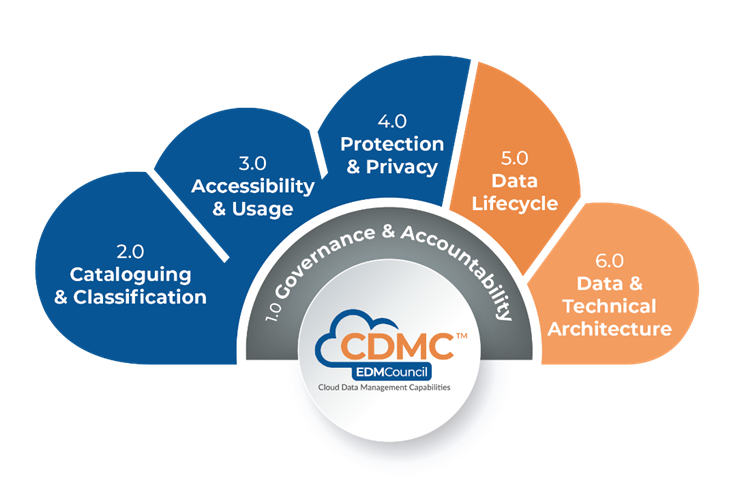
CDMC captures the requirements for these capabilities in six areas. These six Components of the framework include 14 Capabilities and a total of 37 Sub-capabilities. The definition and scope of each component are presented below:

1.0 Governance & Accountability
The Governance & Accountability component is a set of capabilities that ensure an organization has clear accountability, controls and governance for data migrated to or created in cloud environments. These capabilities provide the foundation of well-governed business cases, effective data ownership, governance of data sourcing and consumption and management of data sovereignty and cross-border data movement risks.
This CDMC component helps to:
- Define business cases for managing data in cloud environments, including a value realization framework.
- Ensure that the roles and responsibilities of data owners extend to data in cloud environments.
- Ensure that data sourcing is managed with authoritative sources and authorized distributors.
- Exploit opportunities for automation in the cloud environment to support governance of data consumption.
- Improve understanding of the requirements for managing data sovereignty and cross-border data movement risks.
- Implement controls for data sovereignty and cross-border data movement risk.
2.0 Cataloguing & Classification
The Cataloging & Classification component is a set of capabilities for creating, maintaining and using data catalogs that are both comprehensive and consistent. This component includes classifications for information sensitivity. These capabilities ensure that data managed in cloud environments is easily discoverable, readily understandable and supports well-controlled, efficient data use and reuse.
This CDMC component helps to:
- Define the scope and granularity of data to be cataloged.
- Define the characteristics of data as metadata.
- Catalog the data and the data sources.
- Connect the metadata among multiple sources.
- Share metadata with authorized users to promote discovery, reuse and access.
- Enable sharing of metadata and data discovery across multiple catalogs, platforms and applications.
- Define, apply and use the information sensitivity classifications.
3.0 Accessibility & Usage
The Accessibility & Usage component is a set of capabilities to manage, enforce and track entitlements and to ensure that data access, use and outcomes of data operations are done in an appropriate and ethical matter.
This CDMC component helps to:
- Express and capture data rights and obligations as metadata.
- Ensure that parties respect data rights and obligations over data they are entitled to access.
- Track and report on data access for both regulatory compliance and billing purposes.
- Establish formal organization structures for oversight of data ethics.
- Operationalize ethical access and use of data and ethical outcomes of data decisions.
4.0 Protection & Privacy
The Protection & Privacy component is a set of capabilities for collecting evidence that demonstrates compliance with the organizational policy for data sensitivity and protection. The purpose of these capabilities is to ensure that all sensitive data has adequate protection from compromise or loss as required by regulatory, industry and ethical obligations.
This CDMC component helps to ensure that:
- Data loss protection regimes are implemented.
- Evidence is gathered to demonstrate the application of required data security controls has been accomplished.
- A data privacy framework is defined and approved.
- A data privacy framework is operational.
- Data obfuscation techniques are applied to all data types according to classification and security policies.
5.0 Data Lifecycle
The Data Lifecycle component is a set of capabilities for defining and applying a data lifecycle management framework and ensuring that data quality in cloud environments is managed across the data lifecycle.
This CDMC component helps to:
- Define, adopt and implement a data lifecycle management framework.
- Ensure that data at all stages of the data lifecycle is properly managed.
- Define, code, maintain and deploy data quality rules.
- Implement processes to measure data quality, publish metrics and remediate data quality issues.
6.0 Data & Technical Architecture
The Data & Technical Architecture component is a set of capabilities for ensuring that data movement into, out of and within cloud environments is understood and that architectural guidance is provided on key aspects of the design of cloud computing solutions.
This CDMC component helps to:
- Establish and apply principles for data availability and resilience.
- Support business requirements for backup and point-in-time recovery of data.
- Facilitate optimization of the usage and associated costs of cloud services.
- Support data portability and the ability to migrate between cloud service providers.
- Automate identifying data processes and flows within and between cloud environments while capturing metadata to describe data movement as it passes along the data supply chain.
- Identify, track and manage changes to data lineage, and provide the ability to explain lineage at a point-in-time.
- Provide tooling to report and visualize lineage such that the outputs are meaningful from a business and technical perspective.
Structure of CDMC
As introduced above, CDMC is organized into six components. Each component is preceded with a definition that describes the components, explains why it is important and explains how it relates to the overall cloud data management process. These definitions are written for business and operational executives to understand the cloud data management process better. The components are organized into 14 capabilities and 37 sub-capabilities. The capabilities and sub-capabilities are the essences of the CDMC Framework. They define the goals of data management at a practical level and establish the operational requirements that are needed for sustainable cloud data management. Each sub-capability has a corresponding set of measurement criteria. The measurements are used in an assessment of your cloud data management journey.
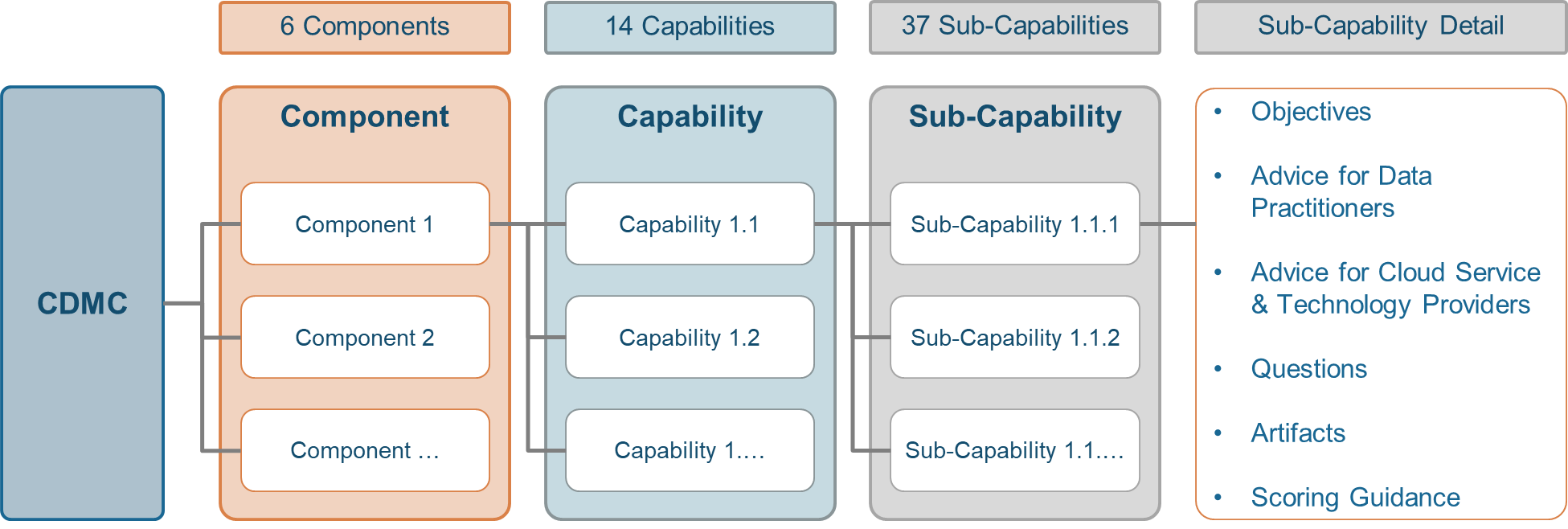
- Component – a group of capabilities that together deliver a foundational tenet of cloud data management. A component functions as a reference guide for data practitioners who are accountable for executing the tenet.
- Upper Matter – high-level context for the component—used as a background for understanding the component by data practitioners.
- Definition – formal description of the component—supporting common data management understanding and language.
- Scope – a set of statements to establish the guardrails for what is included in the component—used to understand and communicate reasonable boundaries.
- Overview – more detailed context and accounting at a practical level to understand the operational execution required for sustainable cloud data management—used as a guide by the respective data practitioners.
- Value Proposition – a set of statements to identify the business value of delivering the cloud data management component—used to inform the varied business cases for developing the data management initiative.
- Core Questions – high-level but probing inquiries—used to explore the cloud data management component.
- Core Artifacts – artifacts required to execute the capability—used to understand deliverables required to support the capability.
- Capability – a group of sub-capabilities that together execute tasks and achieve the stated objectives used as a reference tool by the data practitioners accountable for the execution.
- Description – brief aggregate explanation of what is included in the sub-capabilities required to achieve the capability—used in the assessment process to inform the respondent of the scope of what they are rating.
- Sub-Capability – more granular activities required to achieve the capability—used as a reference tool by the data practitioners accountable for the execution.
- Description – a brief explanation of what is included in the sub-capability—used in the assessment process to inform the respondent of the scope of what they are rating.
- Objective – identified goals or desired outcomes from executing the sub-capability—used as a basis for defining cloud data management process design requirements.
- Advice for Data Practitioners – more detailed but casual insight on the best practices of how to execute the sub-capability with an audit review perspective—used by the data practitioner.
- Advice for Cloud Service and Technology Providers – more detailed but casual insight on how cloud technologies can support the sub-capability—used by cloud service and technology providers.
- Questions – inquiries to direct interrogation of the capability/sub-capability current-state—used by the data practitioner to inform a perspective of the assessment scoring.
- Artifacts – required documents or evidence of adherence—used for assessment and audit reference and to link to supporting best practice material—when available.
- Scoring Guidance – insight for defining an assessment score—used when completing an assessment survey.
Each CDMC Component includes references to Key Controls & Automations, which are specifications of key controls that must be established at the capability level and highlight opportunities to support the control with automation. These are used as a reference tool by data practitioners accountable for the controls and cloud service and technology providers who support their implementation and automation.
CDMC Use Cases
Organizations can use CDMC in multiple ways:
- As a well-defined control framework.
- As a tool to assess readiness for migration to and operation in cloud environments.
- As a certification model for cloud service and technology consumers.
- As a certification model for cloud service and technology providers.
Framework
When an organization adopts the standard CDMC Framework, it introduces a consistent understanding and way of describing cloud data management. CDMC is a comprehensive framework—presented as a best practice paradigm—of the capabilities required to manage data in single, multiple and hybrid cloud environments. It helps accelerate the development of a cloud data management initiative and make it operational. The CDMC Framework:
- Provides a common and measurable cloud data management framework.
- Establishes common language for the practice of cloud data management.
- Translates industry experience and expertise into operational standards.
- Documents cloud data management capability requirements.
- Proposes evidence-based artifacts.
Assessment
Performing an assessment measures the readiness of an organization to migrate to and operate in cloud environments. The assessment produces results that translate the practice of cloud data management into a quantifiable science. The benefits that an organization can gain from assessment outcomes include:
- Baseline measurement of the cloud data management capabilities in the organization compared to an industry standard.
- Quantifiable measurement of the organization’s progress in establishing the required cloud data management capabilities into its operations.
- Identification of cloud data management capability gaps to inform a prioritized roadmap for future development and improvement.
- Focused attention to the funding requirements of the cloud data management initiative.
Effective use of the CDMC Framework as an assessment tool requires the definition of the assessment objectives and strategy, planning for the management of the assessment and adequate training of the participants to establish a base understanding of the framework. Organizations may either perform a self-assessment or may engage the services of a CDMC Authorized Partner to perform an independent assessment.
CDMC Scoring Guide
The CDMC Framework is designed to assess which phase of attainment the organization reaches for each capability. It is not an assessment of the maturity or scope to which the organization has applied the capabilities. The scoring scheme used throughout the framework is as follows:
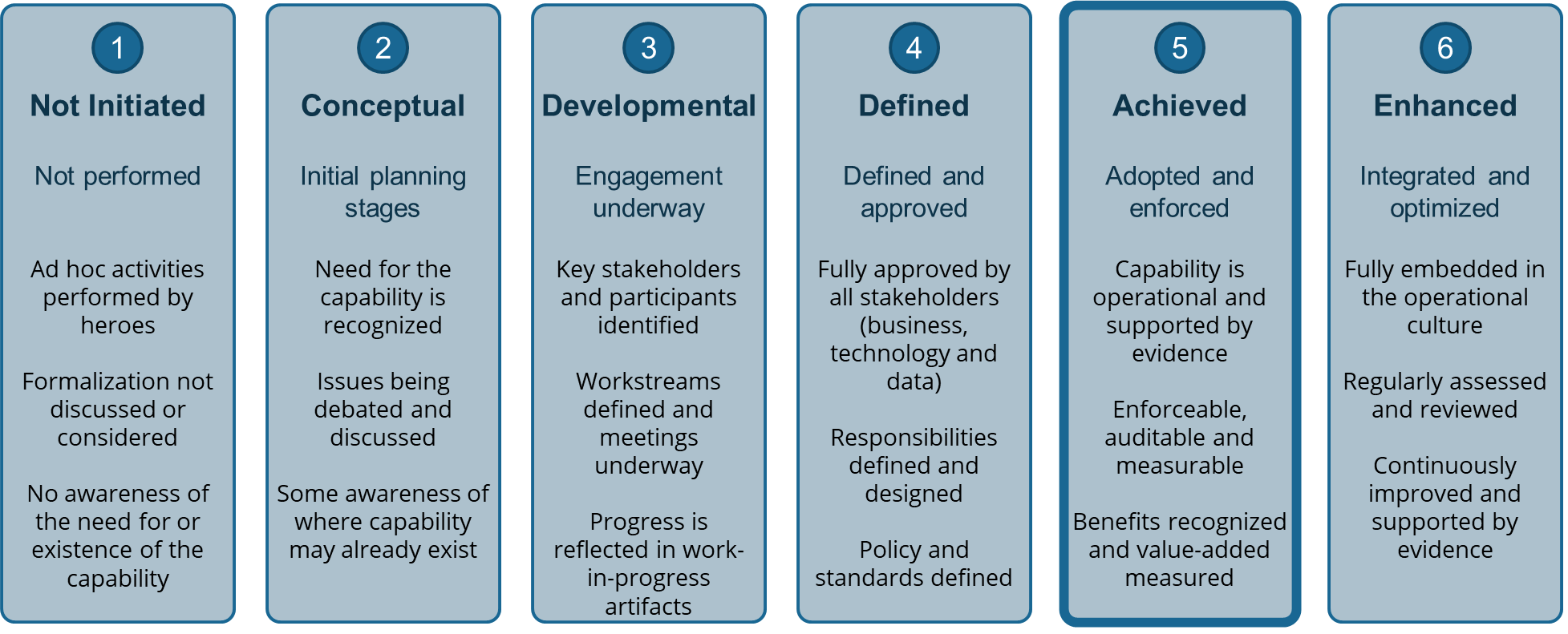
A CDMC assessment must also examine if the key controls have been established. This measurement provides a binary result for each control—the control is either established or not established.
Certification - Consumers
Organizations that achieve all capabilities and establish all key controls can obtain the CDMC Certification. This certification process involves an independent assessment of the achievement of the capabilities and the existence of the controls performed by a CDMC Authorized Partner. If successful, the organization receives a CDMC digital certificate issued by the EDM Council and remains valid for 12 months. This certification is similar to other cloud computing certification programs such as SOC2.
Certification - Providers
Cloud service providers or cloud technology and solution providers can subject their platforms and products to a certification assessment against all or relevant CDMC Key Controls elements to protect sensitive data in cloud environments. An independent CDMC Authorized Partner must perform this certification assessment. Upon successfully completing a certification assessment, the EDM Council will issue a CDMC digital certificate that remains valid for 12 months. This certificate can be commercially represented in the market to indicate that the platform or product supports the respective CDMC Key Controls.
Support Materials
Additional materials support the CDMC Framework presented in this document in the following resources.
CDMC Controls Test Specifications
Specifications of the CDMC Key Controls tests within the framework form the basis of cloud products and services certification against the framework.
Reference: CDMC Controls Test Specification Version 1.1 – to be published Q4 2021
CDMC Information Model
An ontology that draws on and combines related open frameworks and standards to describe the information required to support cloud data management. This ontology provides a foundation for the interoperability of data catalogs and automation of controls across cloud service and technology providers.
Reference: CDMC Information Model Version 1.1 – to be published Q4 2021
CDMC Management Requirements Model
A generic model of data management requirements with mappings to both CDMC and DCAM capabilities shows the relationship and dependencies CDMC capabilities have on basic data management capabilities.
Reference: Data Management Requirements Model V1.1 – to be published Q4 2021
Training
The EDM Council and Authorized Partners offer a 2-day training course on the CDMC Framework.
Reference: https://edmcouncil.org/page/CDMCTraining
Business Glossary
The EDM Council has developed a data management business glossary containing approximately 200 data management term names and definitions. CDMC v1.1 has applied these terms consistently across the document. Where a term is defined in the glossary, the word or phrase is italicized and underlined in the text.
The business glossary is available via the following link: https://edmcportal.org/glossary/.
